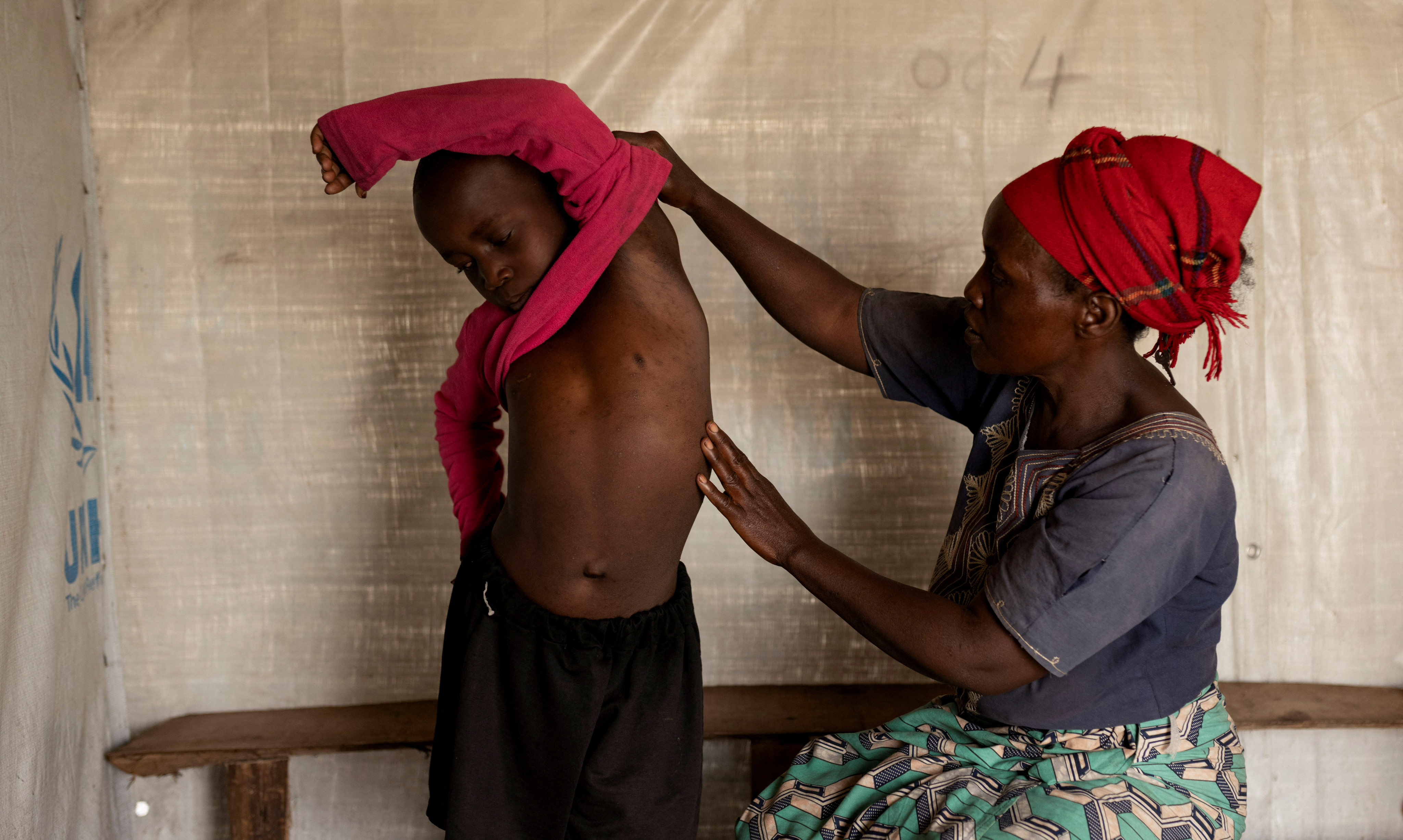TOPIC
Mpox
Mpox
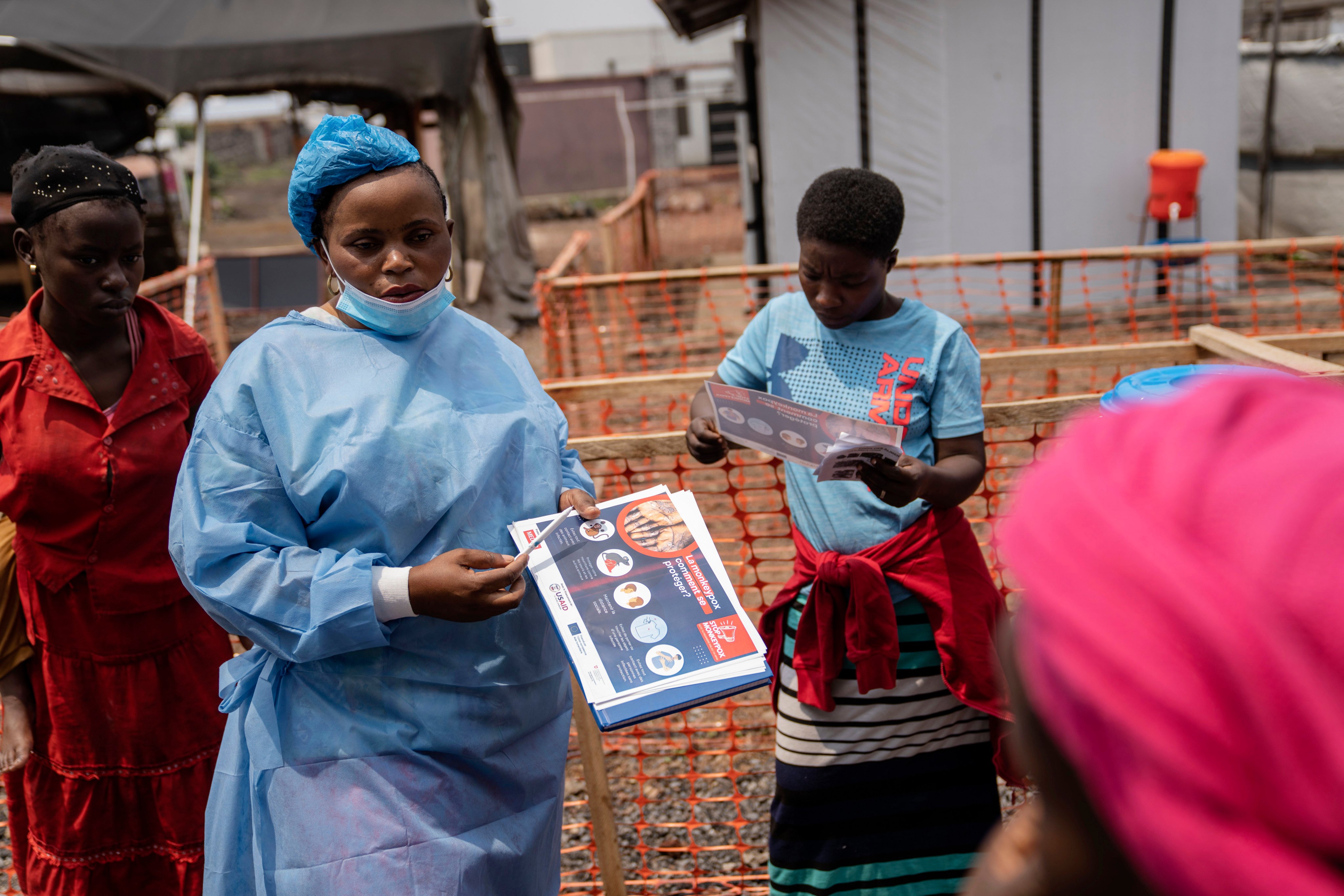
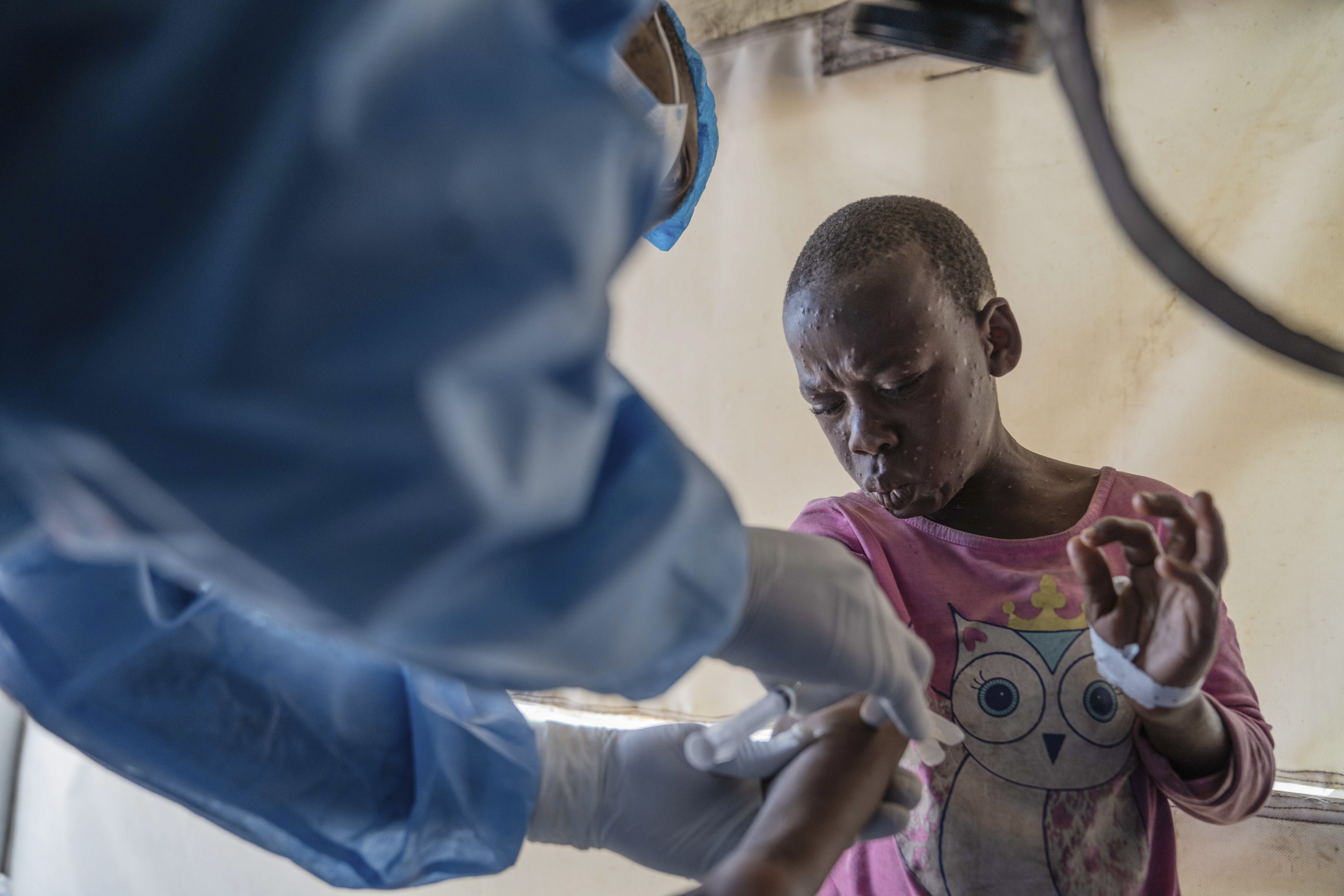
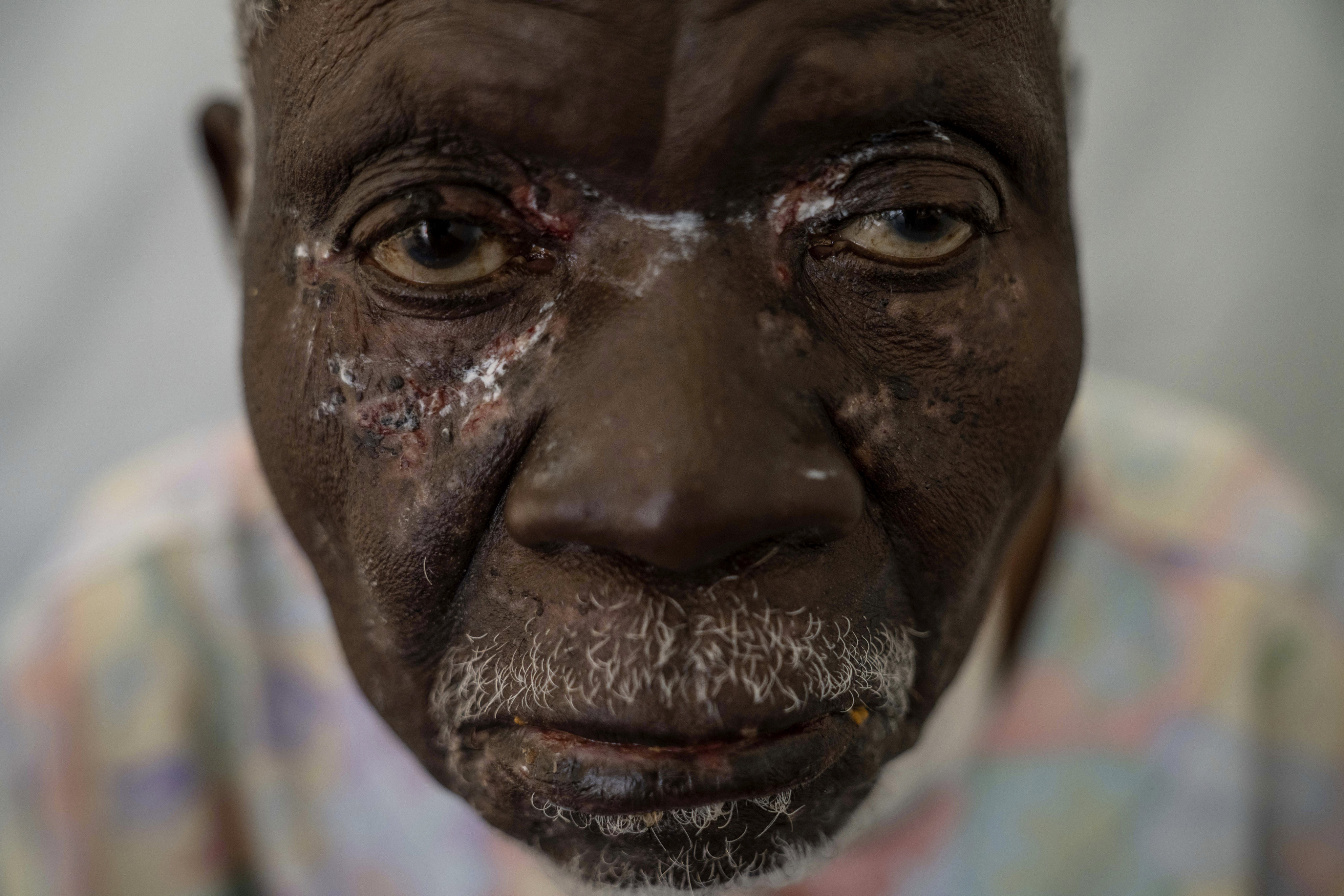
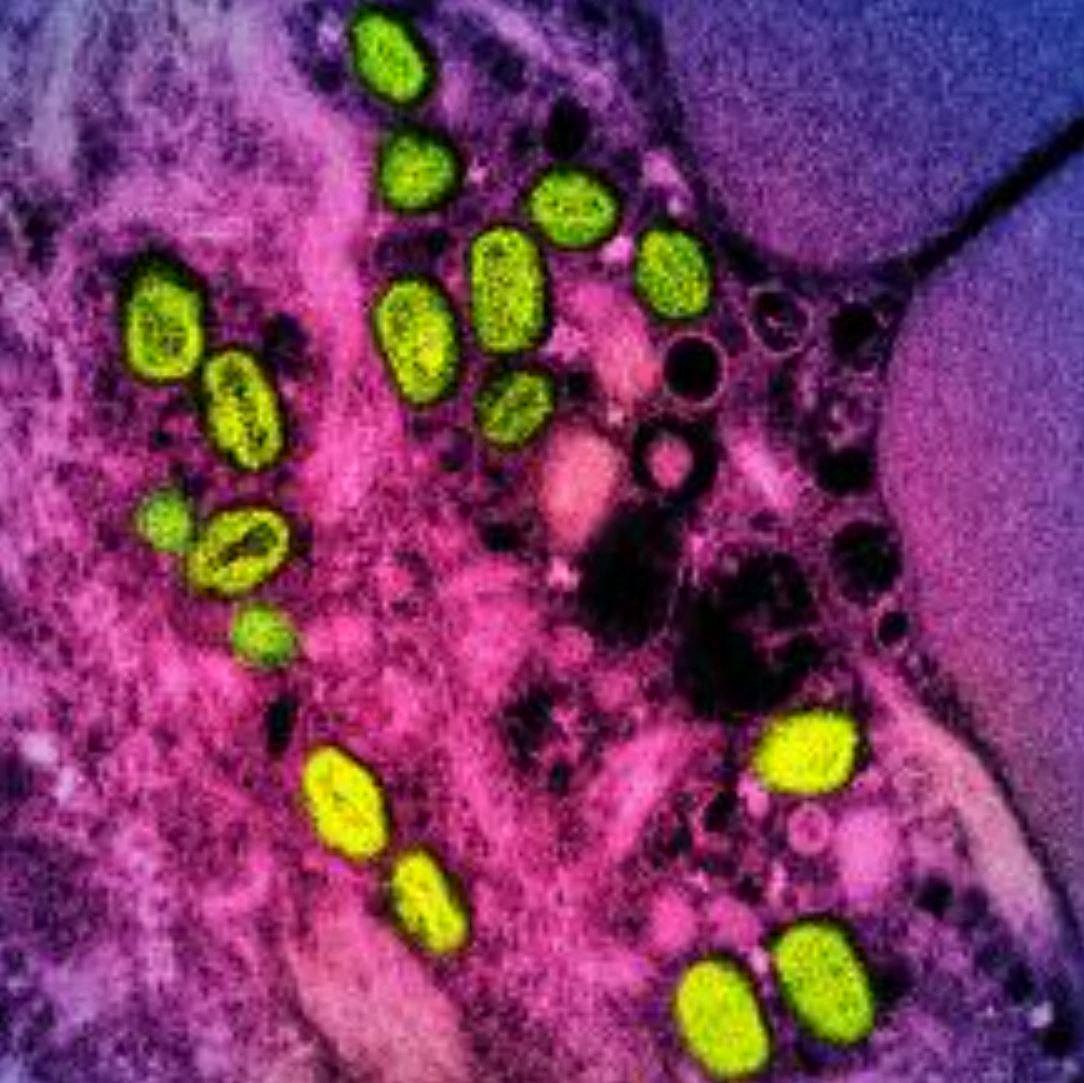
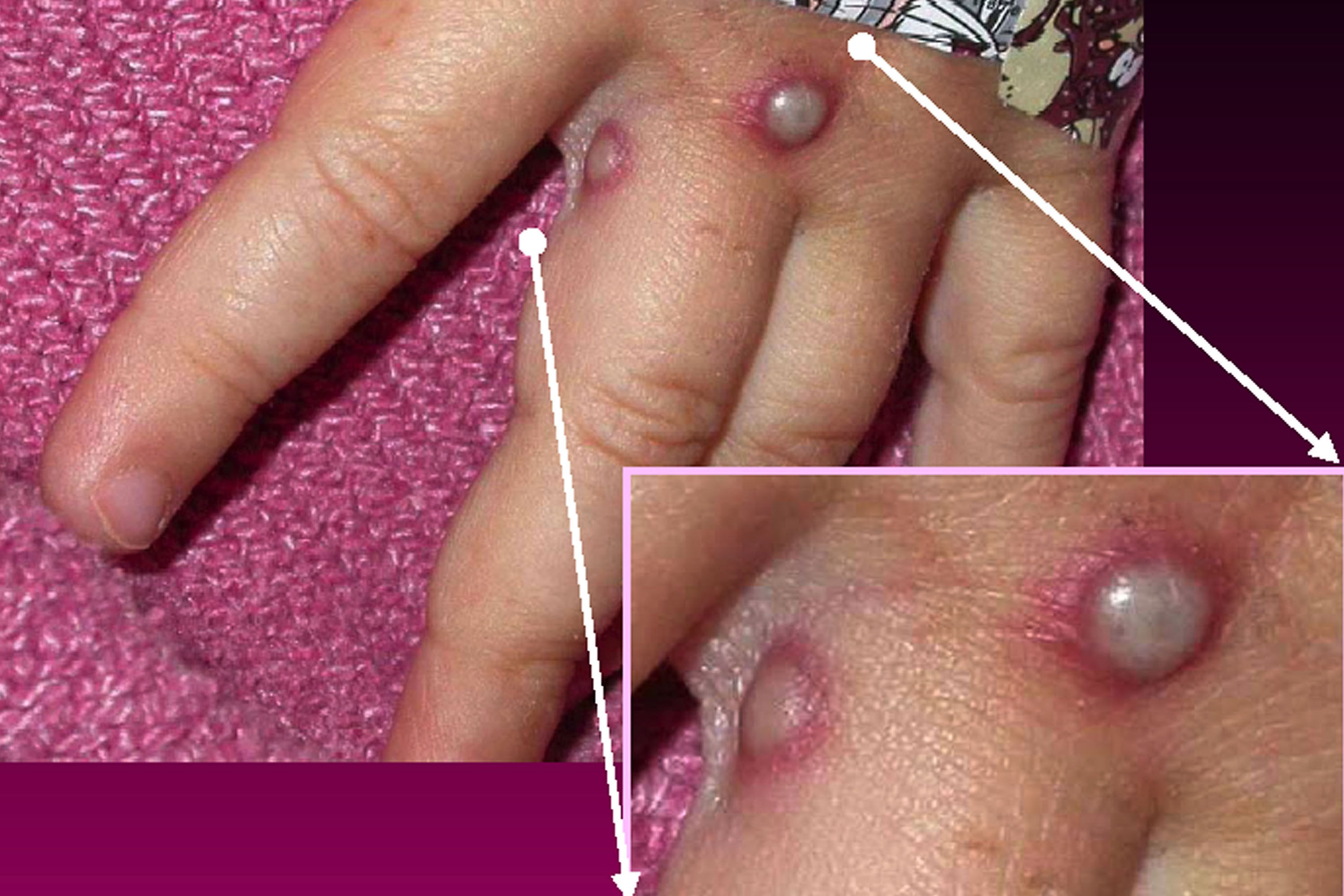
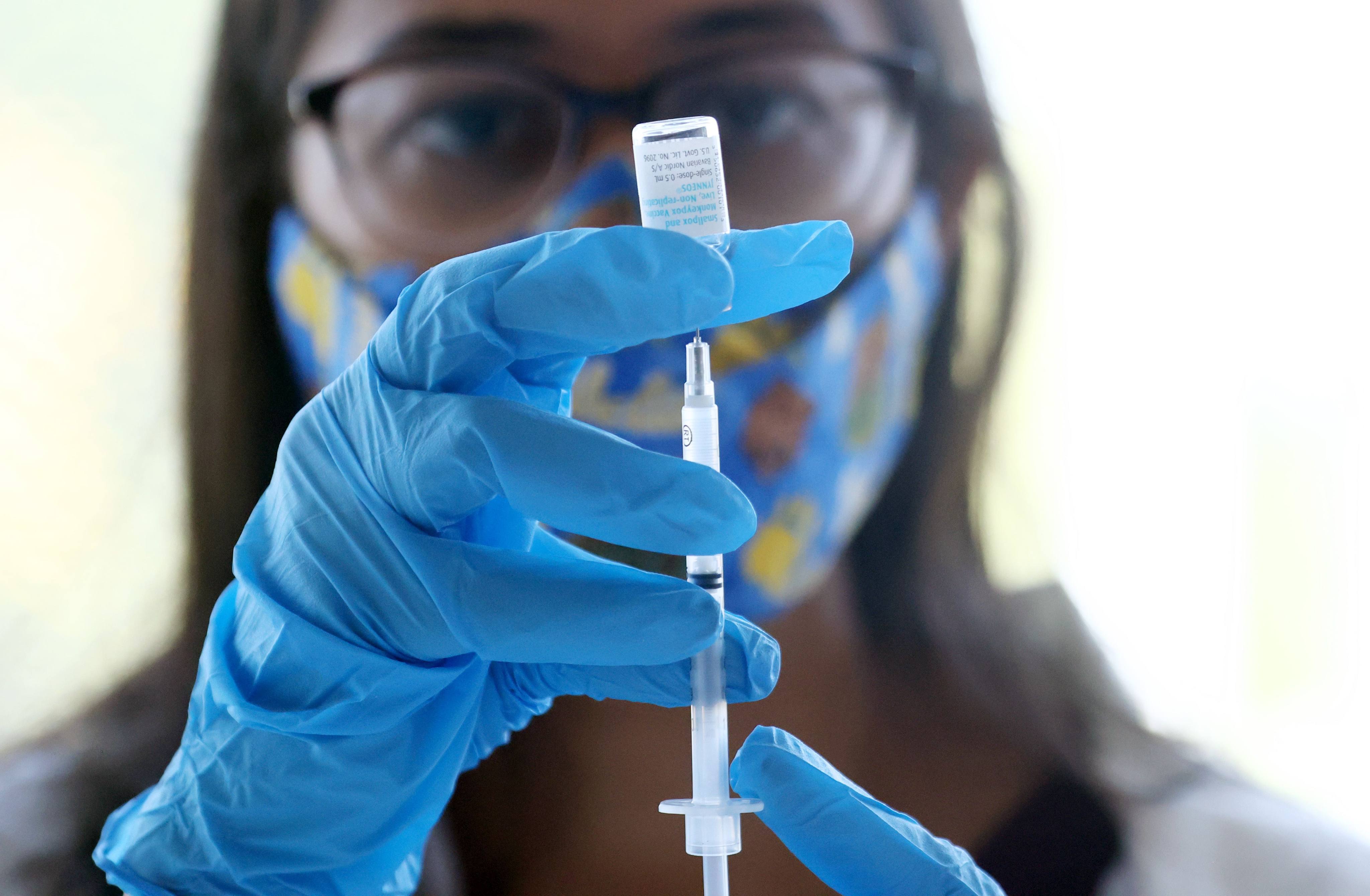
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a viral disease typically spread by contact with wild animals that occurs mostly in central and western Africa. It was called monkeypox because it was first identified in laboratory monkeys, but it typically circulates in small rodents, and can be transmitted to humans, with vectors including bushmeat, an animal bite or scratch, body fluids, contaminated objects, or close contact with an infected person. In 2024, an mpox outbreak in Africa was declared a global health emergency by the WHO.
last updated:
9 September, 2024
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Help preserve 120 years of quality journalism.
SUPPORT NOWAdvertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement