Chinese team’s cell turns ambient heat into power – no sunlight required
Researchers say their sealed hydrovoltaic cell could be used in harsh environments like deserts and in the dark

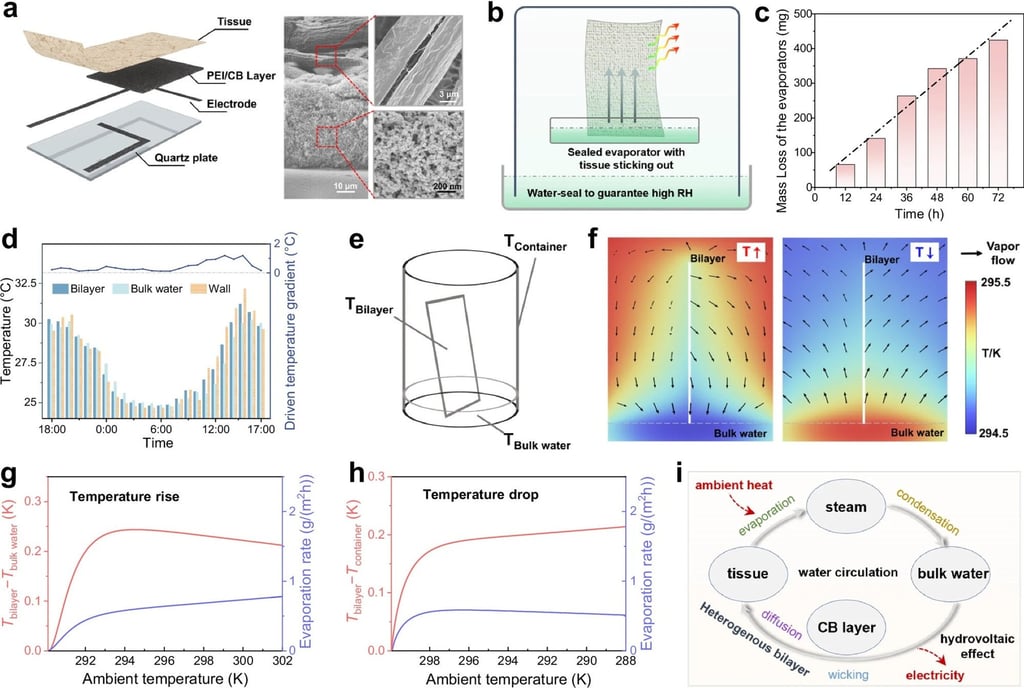
Chinese researchers say they have found a way to continuously produce electricity from water within a sealed container, drawing heat from the surrounds to create vapour for power generation.
While solar-based hydrovoltaic cells need sunlight to work, the team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences say their cell does not – and its resistance to wind and humidity means it could be used in harsh environments like deserts and in the dark.
“We fabricate a hermetic hydrovoltaic cell (HHC) to harvest ambient heat and have fully addressed the limitations posed by environmental conditions,” the team wrote in a paper published in peer-reviewed journal Nature Communications on November 12.
“We anticipate that the hermetic hydrovoltaic cell and the internal circulation hydrovoltaic effect enables the generation of electricity with low cost, easy accessibility, and wide applicability.”
They said their cell achieved stable electricity output for 160 hours with negligible water consumption, which could make it a good candidate for extreme environments like water-scarce deserts, humid tropical rainforests and underground engineering sites.